Zoonoses
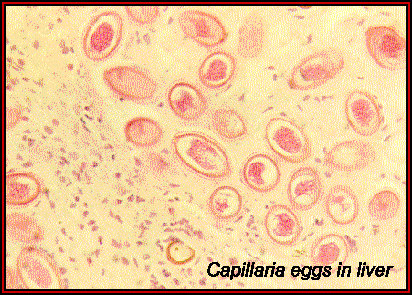 |
Capillaria spp.: This parasite
is found primarily in rodents, although it has been reported in canines and
humans. As the parasite's name implies, the worms live in the host's liver,
generally surrounded by a connective tissue capsule. The adult female produces
eggs, but few of these eggs are passed in the host's feces. Rather, most of
the eggs are deposited in the liver parenchyma, only to be released when the
infected host is eaten by a predator. The eggs are then liberated from the liver
tissue and passed in the predator's feces. Once returned to the soil, the eggs
are ingested by the next host and hatch in the small intestine. The larvae (juveniles)
penetrate into the tissues of the small intestine, enter the portal circulation,
and are transported to the liver. Once in the liver the juveniles grow into
sexually mature adults. As noted above, this parasite has been reported from
humans. In humans, this parasite has also been implicated as a cause of visceral
larval migrans (VLM).

