Chapter 8 - Arrays and Array Processing
|
Chapter Objectives:
You should be able to:
- Use array data structures.
- Solve problems that require collections of data.
- Sort an array of data.
- Demonstrate your understanding of sequential and binary search algorithms.
- Demonstrate your understanding of inheritance and polymorphism.
|
Index:
|
Introduction
- An array is a named collection of contiguous storage locations holding
data of the same type.
- Arrays elements: referenced by position within a structure rather
than by name.
- Example: 7 images to animate CyberPet.
- Without arrays:
g.drawImage(image1, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image2, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image3, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image4, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image5, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image6, 1, 1, this);
g.drawImage(image7, 1, 1, this);
- With arrays:
for (int k = 1; k <= 7; k++)
g.drawImage(image[k], 1, 1, this);
One Dimensional Arrays
- An array element is referred to its position within the array.
- For an n-element array named arr, the elements are named arr[0],
arr[1], arr[2], ...,arr[n-1].
- Arrays are zero indexed, that is, the first element in the array
is referenced as number zero.
- Array syntax : arrayname [ subscript ] where arrayname
is the array name and subscript is an integer giving the element’s relative
position.
- Subscripted array variables are used like other variables:
arr[0] = 5;
arr[5] = 10;
arr[2] = 3;
strings[0] = "who";
strings[1] = "what";
strings[2] = strings[3] = "where";
- Loops can be used to initialize them:
for (int k = 0; k < arr.length;
k++) // printout the contents of arr
System.out.println(arr[k]);
- Valid References: suppose array "arr" has 15 elements and j is 5
and k is 7.
arr[4] //
Refers to 16
arr[j] // Is arr[5] which refers to 20
arr[j + k] // Is arr[5+7] which is arr[12] which refers to
45
arr[k % j] // Is arr[7%5] which is arr[2] which refers to
-1
- Invalid References:
arr[5.0] //
5.0 is a float and can't be an array subscript
arr['5'] // '5' is a character not
an integer
arr["5"] // "5" is a string not an
integer
arr[-1] // Arrays cannot have
negative subscripts
arr[15] // The last element of arr
has subscript 14
arr[j*k] // Since j*k equals 35
- Arrays are (mostly) treated as objects:
- Instantiated with the new operator.
- Have instance variables (e.g., length).
- Array variables are reference variables.
- As a parameter, a reference to the array is passed rather than copies
of the array’s elements.
- But…there is no Array class. So arrays don’t fit into the Object hierarchy.
- Array terminology:
- An empty array is contains zero variables.
- The variables are called components.
- The length of the array is the number of components it has, the
length is referenced using the array name followed by ".length" e.g.
- System.out.println("Array arr
has "+arr.length+" elements"); // print out the length of
arr
- Each component of an array has the same component type.
- A one-dimensional array has components that are called the array’s elements.
Their type is the array’s element type.
- An array’s elements may be of any type, including primitive and reference
types.
Declaring and creating an Array
- Creating a one-dimensional array: Indicate both the array’s element type
and its length.
- Declare the array’s name and create the array itself.
int arr[]; //
Declare a name for the array
arr = new int[15]; // Create the array itself
- Combine two steps into one:
Creating an array of objects (e.g.
String)
- Declared and created similarly to ints however, ...
- Creating a new array of objects does not also create the objects that
are stored in the array.
- They must be instantiated separately.
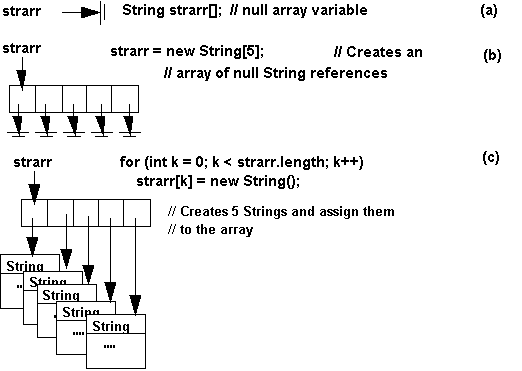
- Example: Create an array of 5 strings
String strarr[]; //
Declare a name for the array
strarr = new String[5]; //
Create the array itself
//
Assign strings to the array
for (int k = 0; k < strarr.length; k++) // For each array
element
strarr[k] = new String("hello" + k + 1); // Assign
it a new string
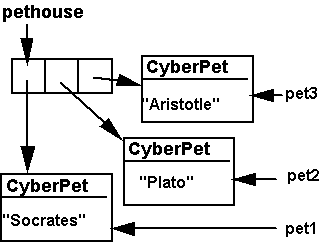
Creating an Array of CyberPets
- the code:
CyberPet pethouse[] = new
CyberPet[3];
// Create an array of 3 CyberPets
pethouse[0] = new CyberPet("Socrates"); // Create the first CyberPet
pethouse[1] = new CyberPet("Plato"); // Create
the second CyberPet
pethouse[2] = new CyberPet("Aristotle"); // Create the third CyberPet
Initializing Elements
- Array elements are initialized to default values:
- Integer and real types are initialized to 0.
- Reference types (objects) are initialized to null.
- Arrays can be assigned initial values when they are created:
- examples:
int arr[] = { -2,8,-1,-3,16,20,25,16,16,8,18,19,45,21,-2
} ;
String strings[] = { "hello", "world", "goodbye", "love"};
- When an array initialization expression is used, don’t use the keyword
new to create the array.
- This works well for relatively small arrays. Large arrays should either
be computer or read in from datafiles or databases (see chapter 14)
Passing arrays as arguments to methods
- Pass by Value: When a value of primitive type is passed to a method,
a copy of the value is passed. Any changes to the copy, have no effect on
the original value.
- Pass by Reference: When a reference to an object (e.g., an array)
is passed to a method, changes made to the object do persist beyond
the method.
Example: Store the First 100 Squares (figure
8-6)
public class Squares
{
static final int ARRSIZE = 100;
// The array's size
static int intArr[] = new int[ARRSIZE]; // Create
an int array
public
static void main(String args[]) {
for (int k = 0; k < intArr.length;
k++) // Initialize the array
intArr[k]
= (k+1) * (k+1);
System.out.print("The first 100 squares are"); // Print heading
for (int k = 0; k < intArr.length;
k++)
{
// Print the array
if (k %
10 == 0)
System.out.println(" "); //
10 elements per row
System.out.print(
intArr[k] + " ");
} // for
} // main()
} // Squares
Program Output:
The first 100 squares are
1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81 100
121 144 169 196 225 256 289 324 361 400
441 484 529 576 625 676 729 784 841 900
961 1024 1089 1156 1225 1296 1369 1444 1521 1600
1681 1764 1849 1936 2025 2116 2209 2304 2401 2500
2601 2704 2809 2916 3025 3136 3249 3364 3481 3600
3721 3844 3969 4096 4225 4356 4489 4624 4761 4900
5041 5184 5329 5476 5625 5776 5929 6084 6241 6400
6561 6724 6889 7056 7225 7396 7569 7744 7921 8100
8281 8464 8649 8836 9025 9216 9409 9604 9801 10000
Random Number Generation
- Math.random() is a method
that returns a double value between 0 and .99999999
- When called some number of times, generates each of the numbers in a relatively
equal distribution.
- Note: Not truly random, unless new seed is provided
- To simulate a coin flip, must convert returned value to either 0 or 1
int coinFlip = (int)(Math.random()
* 2);
- Note that using any scaling factor N will convert the random values to within
the range [0, N-1]
int coinFlip = (int)(Math.random()
* N);
- If N is 6, will return values from 0-5. If we want to return values from
1-6, such as for a Die, we just need to add 1 to the expression:
int die = 1 + (int)(Math.random() *
6);
- In general, to generate a set of N values in the range M to M + N -1, use
the expression:
M + (int)(Math.random() * N);
Example: Simulating throwing a Die
public void testDie(int nTrials) {
int die; // Represents the die
for (int k = 0; k < nTrials;
k++) { // For each trial
die =
1 + (int)(Math.random() * NFACES); // Toss the die
++counter[die
- 1]; // Update the appropriate counter
} // for
} //testDie()
View complete
TestDie application code.
CyberPet Animation
- Problem: Animate CyberPet.
- Problem Decomposition: An applet loads the images into an array.
Then draws them with a short delay.
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
public class Animate extends
Applet {
private static int NIMAGES = 5;
private static int MILLISECS = 200;
private Image image[] = new Image[NIMAGES];
private int imageN = 0;
public
void init() {
showStatus("Loading image files.
Please wait.");
for (int k = 0; k < image.length;
k++) // Load images from files
image[k]
= getImage(getDocumentBase(), "spider" + k + ".gif");
} // init()
public
void paint(Graphics g) {
g.drawImage(image[imageN], 1,
1, this); // Draw an image
imageN = (imageN + 1) % NIMAGES; //
Select the next image
delay(MILLISECS); //
Delay for a while
repaint(); //
Then do it all over again
} // paint()
} // Animate
Click here to view the applet
Array Algorithm : Sequential Search
- Problem: Search an array for a key value. If the array is not sorted, we
have to search sequentially. That is, we must start at the beginning of the
array and check each element until we find the one we want.
/**
* Performs a sequential search of an integer array
* @param arr is the array of integers
* @param key is the element being searched for
* @return the key's index is returned if the key is
* found otherwise -1 is returned
* Pre: arr is not null
* Post: either -1 or the key's index is returned
*/
public int sequentialSearch(int
arr[], int key) {
for (int k = 0; k < arr.length; k++)
if (arr[k] == key)
return
k;
return -1; // Failure
} // sequentialSearch()
- Variation: Search an array for the minimum value:
/**
* Performs a sequential search of an integer array
* @param arr is the array of integer
* @return the smallest integer in the array
* found otherwise -1 is returned
* Pre: arr is not null
* Post: either -1 or the key's index is returned
*/
public int sequentialMin(int arr[]) {
int smallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // smallest
will find the minimum number, start it at the largest possible
for (int k = 0; k < arr.length; k++)
if (arr[k] < smallest)
smallest
= arr[k];
return smallest; // return the
smallest number
} // sequentialMin()
Array Algorithms : Sorting
- Bubble Sort: takes a lot of time because all elements are checked with multiple
passes through the array
- Each 2 elements are compared, and if out of order, are swapped
30 3 45 -6 15 //first pass
3 30 -6 15 45 //second pass
3 -6 15 30 45 //third pass
-6 3 15 30 45 //fourth pass
- Requires swapping method:
public void swap(int arr[],
int el1, int el2) {
int temp = arr[el1];
//assign the first element to temp
arr[el1] = arr[el2]; //overwrite first with second
arr[el2] = temp; //overwrite second with first
(temp)
} // swap()
View Bubble Sort code
Selection Sort Algorithm
- To sort in ascending order: On each pass, find the smallest remaining value
in the original array, and place in next location in result array
- Takes less time than bubble sort (more efficient)
Algorithm:
- For count = 1 to 51
- smallest card = count
- For currentCard = count+1 to 52
- If deck[currentCard] < deck[smallestCard]
- smallestCard = CurrentCard
- If smallestCard != count
- Swap deck[count] and deck[smallestCard]
Binary Search
- Requires sorting array elements first (either ascending or descending)
- Then don't have to search every element - can simply compare with lowest
and highest values in a range to find out if within that range
Example: find out if "7" is in the array {100, 6, 55, 7, 15, 40}
|
intArr[0]
|
intArr[1]
|
intArr[2]
|
intArr[3]
|
intArr[4]
|
intArr[5]
|
|
100
|
6
|
55
|
7
|
15
|
40
|
|
6
|
7
|
15
|
40
|
55
|
100
|
|
low
|
|
mid
|
|
|
high
|
|
low
|
mid
|
high
|
|
|
|
View Search Class
View TestSearch code
Two Dimensional Arrays
Initializing Two Dimensional Arrays
- Two dimensional arrays can be initialized using nested for loops :
/**
* Initializes a 2-D array
* @param rain is a 2D-array of rainfalls
* Pre: rain is non null
* Post: rain[x][y] == 0 for all x,y in the array
* Note that the loops use unit indexing, not zero indexing
*/
public void initRain(double rain[][]) {
for (int month = 1; month < rain.length;
month++)
for (int day = 1; day <
rain[month]Length; day++)
rain[month][day]
= 0.0;
} // initRain()
- To call this method:
initRain(rainfall); // Sample method
call
- Note, the call is passing the array rainfall by reference (not by value),
therefore the method changes the values in the rainfall array.
- Two dimensional arrays can also be initialized at the time they are created:
Example: Calculate
average rainfall
/**
* Computes average daily rainfall
* @param rain is a 2D-array of rainfalls
* @return The sum of rain[x][y] / 356
* Pre: rain is non null
* Post: The sum of rain / 365 is calculated
* Note that the loops are unit indexed
*/
public double avgDailyRain(double rain[][]) {
double total = 0;
for (int month = 1; month < rain.length; month++)
for (int day = 1; day <
rain[month]Length; day++)
total
+= rain[month][day];
return total/365;
} // avgDailyRain()
- Note : rain[3]Length would tell how many array elements (days) there
are for march, rain.length would tell how many element months there
are.
- Challenges:
- How would you fix this code to correctly calculate the average rainfall
on a leap year?
- Could you add a feature that would print out the total number of days
in the year it rained?
- Could you add a feature to print out the day and month and amount of
the day with the most rain?
Example: Calculate average
rainfall for a particular month
/**
* Computes average rainfall for a given month
* @param monthRain is a 1D-array of rainfalls
* @param nDays is the number of days in monthRain
* @return The sum of monthRain / nDays
* Pre: 1 <= nDays <= 31
* Post: The sum of monthRain / nDays is calculated
*/
public double avgRainForMonth(double
monthRain[], int nDays) {
double total = 0;
for (int day = 1; day < monthRain.length; day++)
total = total + monthRain[day];
return total/nDays;
} // avgRainForMonth()
to call...
double rainfall[][] =
new double[13][32];
double marchAvg = avgRainForMonth(rainfall[3],
31); // this passes a reference to a single row in the array
Summary
Keywords:
array, array initializer, array length, binary search, bubble sort, element,
element type, multidimensional array, one-dimensional array, polymorphic method,
pseudorandom number, random , number scaling, selection sort, sequential search,
sorting, subscript
Suggested Exercises: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12, 14, 15, 17, 29